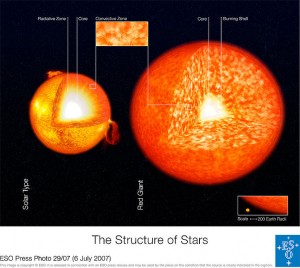
A red giant can be defined as a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (approximately 0.5-10 solar masses) that is in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is puffed up and weak, making the radius immense and the surface temperature low, somewhere from 5000 K and lower. The color of the red giant might vary from yellow orange to red including most carbon stars.
The red giant branch stars (RGB stars) are those whose shells are fusing hydrogen into helium. The core is made of inactive helium. Another type of red giants is the asymptotic giant branch stars (AGB) that produces carbon from helium, instead of hydrogen by the triple-alpha process. Some of the most famous red giants in the sky are
Alpha Tauri
Alpha Bootis
Gamma Crucis
Alpha Scorpio
Features:
First of all, red giants are stars with radii tens to hundreds of times larger than that of the Sun, which have exhausted the supply of hydrogen in their cores and switched to fusing hydrogen in a shell outside the core. But, these stars are not perfect big red spheres with sharp limbs and stuff. The stars may not have a sharp photosphere due to the very low density. So, a star body gradually transfers into a “corona”.
Stellar development:
Basically, the red giants are evolved from the main sequence stars, with masses in the range from about 0.5 solar masses to anywhere between 4 and 6 solar masses. A star is initially formed from a collapsing a molecular cloud in the interstellar medium. The star initially contains primarily hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of metals. All these elements are equally mixed throughout the star. The star then reaches a main phase of its formation, when the temperature of the core reaches a high temperature enough to begin fusing hydrogen and establishing the hydrostatic equilibrium.
Over its sequence of life, the star slowly converts the hydrogen present in the core into helium. The main sequence of its life ends when the entire hydrogen present is converted into helium. This lifetime is about 10 billion years for the Sun. When the hydrogen in the star is exhausted, the nuclear reactions taking place at the core stop. As a result, the core begins to contract due to its gravity.
Certain stars don’t even become a red giant. The reason is that very low mass stars do not accumulate an inert core of helium and thus, may exhaust all of their fuel without even becoming red giants. Since they don’t become red giants, they are known as red dwarfs. The Sun is expected to become a red giant in approximately 5 billion years.